W.A.A.P.A.
Western Australian Academy of Performing Arts
Edith Cowan University
L61 – Dctor of Philosophy
Student # 10888805
This was identified as exceptional research and supported by the Australian Government’s Research Training Program Scholarship.
Please follow this link to view the media files analysed.
Coordinating the Telematic Music Performance Experience with Telemidi: Synchronising Nodes, Enhancing Musicality, and Delivering Simultaneity.
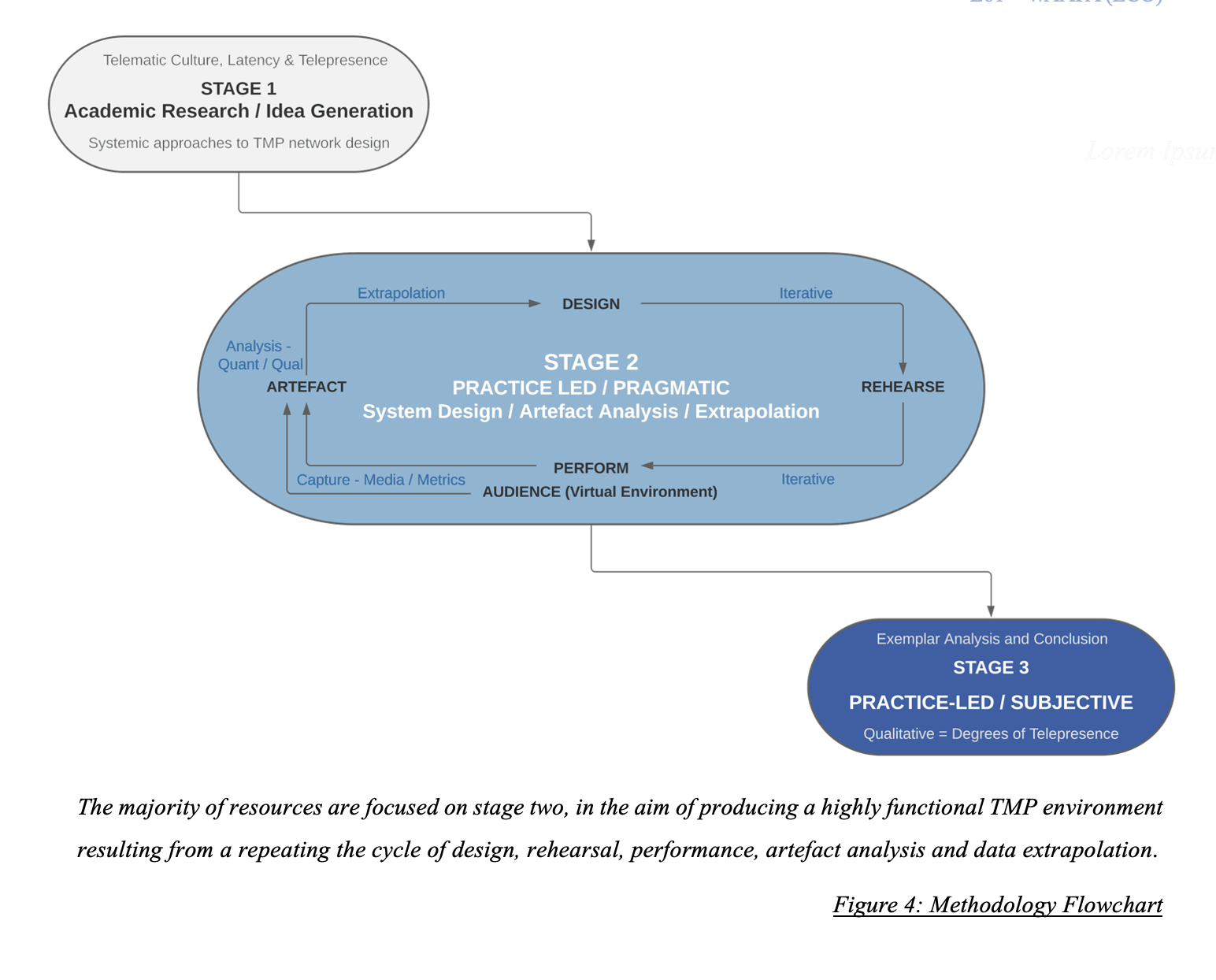
The practice of Telematic Music Performance (TMP), a subset of Network Music Performance (NMP), enables geographically remote musicians to engage in real-time musical interplay, typically occurring over a Wide Area Network (WAN: the Internet). However, the transmission of data between remote collaborators introduces millisecond latencies that obstruct the nuance of traditional human-to-human musical intercourse, and consequentially, the music generated by TMP often lacks rudimentary degrees of syncopation. Reducing network latency has been a critical focal point for research in this field, wherein effective networks support low-latency, multi-modal data transmission to enhance sensations of immersion and telepresence for participants; the sense of sharing the ‘same space’ as their collaborator. The author has previously established Telemidi as an effective approach; a TMP system exchanging only MIDI performance data as a primary Latency Accepting Solution (LAS); used to trigger a series of loop-based rhythmic devices upon which a range of improvised, and performative musical actions may occur. This current research undertakes a broad exploration of literature to identify optimal TMP operations and system designs, before implementing a practice-led methodology to iteratively refine and innovate the Telemidi TMP system; to reduce latency, minimise its influence, and to enhance a performer’s musical actions. By synchronising activity between distributed, and near-identical Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs), this research explores approaches to enable remote collaborators to co-create stable, and progressive Pulse-Based Music (PBM). MIDI data also facilitates detailed metric analysis of performative actions, and provides opportunities to generate reactive, multi-media content as a result of music performance actions. This immersive media output may be experienced by audiences using VR headwear. A successful implementation of this process holds the potential for a wide array of applications including music performance, music education, online gaming, remote medical therapeutics and virtual wellness services.